Maintaining sterility in aseptic filling operations is crucial to ensuring the safety and quality of pharmaceutical products. Aseptic filling involves filling containers, such as vials, syringes, or bottles, with sterile drug products in a way that prevents contamination by microorganisms. It is necessary to follow strict protocols and best practices to maintain sterility throughout the entire process.
Creating a Clean and Controlled Environment
One of the key steps in maintaining sterility during aseptic filling operations is ensuring a clean and controlled environment. This includes using cleanroom facilities that are designed to minimize the presence of contaminants. Cleanrooms are typically equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters that remove airborne particles, as well as maintaining positive air pressure to prevent outside contaminants from entering the room. Employees working in the cleanroom need to wear appropriate sterile garments, such as gowns, gloves, masks, and shoe covers, to prevent shedding of skin particles and microorganisms.
Cleaning and Disinfection of Equipment and Surfaces
Another important aspect of maintaining sterility is proper cleaning and disinfection of equipment and surfaces. All equipment used in Aseptic filling machine operations should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected before and after each use to prevent the build-up of microbial contamination. This includes filling machines, containers, and any tools or materials used in the process. Cleaning procedures should be validated to ensure effectiveness, and disinfectants should be chosen based on their compatibility with equipment and ability to kill a broad spectrum of microorganisms.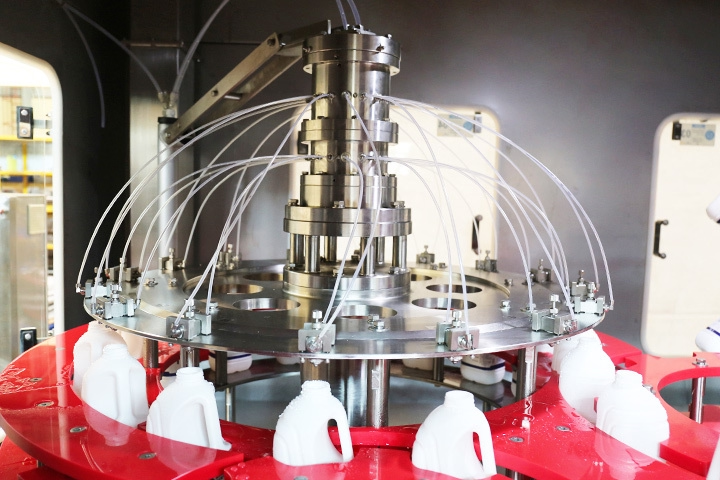
Establishing Strict Aseptic Technique Procedures
In addition to maintaining a clean environment and properly cleaning equipment, it is essential to establish strict procedures for aseptic technique during filling operations. This includes training operators on proper aseptic practices, such as hand washing, gowning, and disinfecting surfaces. Operators should be monitored regularly to ensure compliance with aseptic techniques and to identify any potential sources of contamination.
Monitoring Component Integrity
Furthermore, it is essential to monitor the integrity of sterilized components, such as containers, closures, and filters, throughout the filling process. All components should be inspected for defects or damage that could compromise sterility. Containers and closures should be handled carefully to prevent contamination, and filters should be checked regularly for integrity to ensure they are effectively removing microorganisms.
Establishing a Robust Quality Control System
To further enhance sterility in aseptic filling operations, it is important to establish a robust quality control system. This includes regular monitoring of environmental conditions, such as air quality and microbial contamination levels, to ensure a clean and controlled environment. In-process testing should be conducted to verify the sterility of filled products, and samples should be tested for microbial contamination before release.
Conclusion: Maintaining Sterility in Aseptic Filling Operations
Overall, maintaining sterility in aseptic filling operations requires a comprehensive approach that includes strict adherence to protocols and best practices. By following proper procedures for cleanroom design, equipment cleaning, aseptic technique, component integrity, and quality control, pharmaceutical manufacturers can ensure the safety and efficacy of their products. Effective maintenance of sterility is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring the trust and confidence of patients and healthcare providers.